Enabling the local firewall can protect your device from unwanted connections initiated by other computers when you're connected to a network.
macOS Instructions:
- On your Mac, choose Apple menu > System Preferences, click Security & Privacy, then click Firewall. (Please note: on macOS Ventura or greater the path is Apple menu > System Settings, click Security & Privacy, then click Firewall)
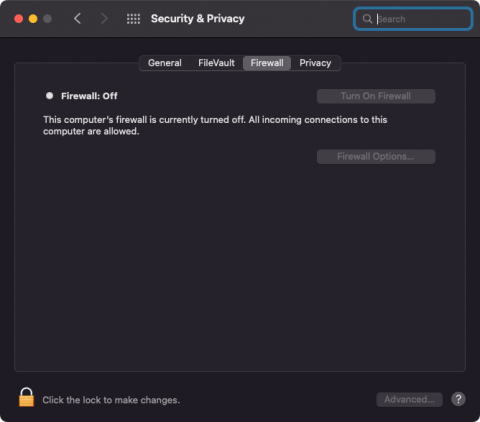
2. Click the lock in the bottom left to make changes.
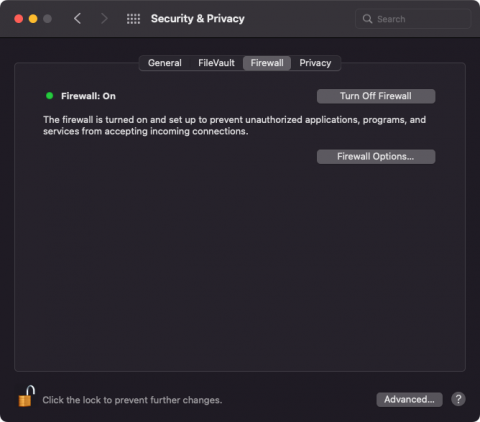
3. Click Turn On Firewall.
Windows Instructions:
The Microsoft Defender Firewall is enabled by default. Turning off Microsoft Defender Firewall could make your device more vulnerable to unauthorized access. If there's an app you need to use that's being blocked, you can allow it through the firewall, instead of turning the firewall off.
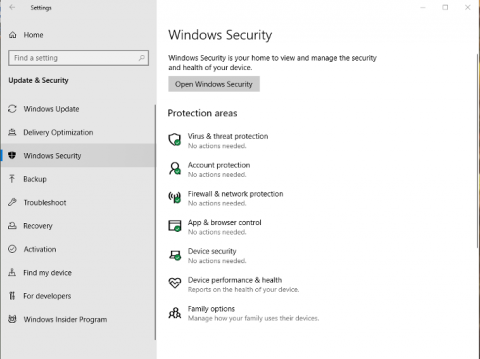
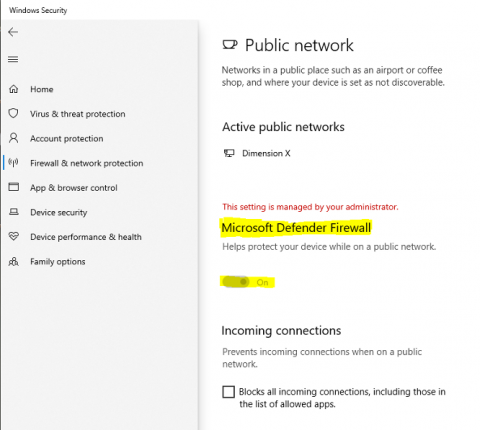
- Select the Start button > Settings > Update & Security > Windows Security and then Firewall & network protection.
-
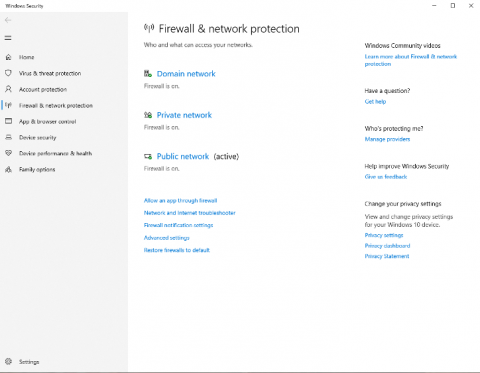
Select a network profile: Domain network, Private network, or Public network.
-
Under Microsoft Defender Firewall, switch the setting to On.
Linux Instructions:
Distributions handle the firewall different some have variation of products, and the others may have turned off the firewall by default. Two popular options are IPTABLES and UFW (Uncomplicated Firewall) both can be installed using a package manager. Based on your Service Manager the steps to check status and/or start will vary – additionally, recall the root user or the sudo setup when running commads.
IPTABLES
IPTABLES is traditionally located in /usr/sbin/iptables it may also be found in /sbin/iptables If your distribution has IPTABLES it may be active, but to verify try the following.
| ~# service iptables status. | |
| OR | |
| ~#systemctl status iptables |
Start it by changing ‘status’ with ‘start’.
UFW (Uncomplicated Firewall) depending on the distribution may be installed but stopped.
To start the services on a Ubuntu distribution or derivative distribution of Ubuntu, keep in mind that Debian may not use sudoers by default.
| :~$ sudo ufw enable | |
| ~$ sudo ufw status verbose |
: